| Uracil/Thymine families |
Earth |
|
| |
| 6. |
n |
 Serine Serine | Ser | S | UCC UCU UCA UCG | 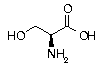 4-Serine: Assist in the manufacture of the organic acid Creatine, found in blood, while also present within muscle and brain tissue as an energy source for muscle contraction. Participant in purine, pyrimidine and porphyrin biosynthesis. Also a natural moisturizing agent used in cosmetics. 4-Serine: Assist in the manufacture of the organic acid Creatine, found in blood, while also present within muscle and brain tissue as an energy source for muscle contraction. Participant in purine, pyrimidine and porphyrin biosynthesis. Also a natural moisturizing agent used in cosmetics. |
| 7. |
19 |
 Phenylalanine Phenylalanine | Phe | F | UUC UUU | 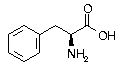 Phenylalanine: Used by the brain as a natural precursor to the manufacture of norepinephrine and other neurotransmitters, it enhances learning, alertness and memory. Also used in the treatment of depression, and the ‘D’ form Phenylalanine acts as a pain killer. Nutritional conflicts may occur unless kept in balance with other amino acids through dietary intake. Phenylalanine: Used by the brain as a natural precursor to the manufacture of norepinephrine and other neurotransmitters, it enhances learning, alertness and memory. Also used in the treatment of depression, and the ‘D’ form Phenylalanine acts as a pain killer. Nutritional conflicts may occur unless kept in balance with other amino acids through dietary intake. |
| n. |
18 |
 Leucine Leucine | Leu | L | UUA UUG | 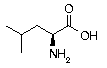 2-Leucine: Must be kept in balance with other amino acids through dietary intake, or nutritional conflicts may occur. Useful in lowering blood sugar levels. It is found in high concentrations in muscle tissue, and promotes wound healing of skin and bone. 2-Leucine: Must be kept in balance with other amino acids through dietary intake, or nutritional conflicts may occur. Useful in lowering blood sugar levels. It is found in high concentrations in muscle tissue, and promotes wound healing of skin and bone. |
|
| 8. |
17 |
 Tyrosine Tyrosine | Tyr | T | UAC UAU | 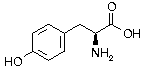 Tyrosine: Direct precursor of adrenaline and thyroid hormones, it helps control depressions and anxiety, and acts as a growth hormone stimulant. Plays an intermediary role in the synthesis of the neurotransmitter Norepinephrine from Phenylalanine. Considered an antioxidant and appetite suppressant. Tyrosine: Direct precursor of adrenaline and thyroid hormones, it helps control depressions and anxiety, and acts as a growth hormone stimulant. Plays an intermediary role in the synthesis of the neurotransmitter Norepinephrine from Phenylalanine. Considered an antioxidant and appetite suppressant. |
|
| 9. |
16 |
Stop codons | X | UAA UAG | I believe there are some still to be discovered microbes, which make another amino acid with this two codons.(see UGA) |
| 10. |
15 |
 Cysteine Cysteine | Cys | C | UGC UGU | 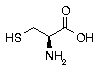 Cysteine: Used to stimulate white blood cell activity in the immune system. Essential for the formation of skin, and promotes healing from cuts and burns. Effective antioxidant and scavenger of free radicals. It is the only Amino acid to form the connections of the protein folding process. Cysteine: Used to stimulate white blood cell activity in the immune system. Essential for the formation of skin, and promotes healing from cuts and burns. Effective antioxidant and scavenger of free radicals. It is the only Amino acid to form the connections of the protein folding process. |
|
| 11. |
14 |

Stop codon or
Selenocysteine | X | UGA | 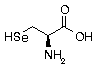 Normally UGA is stop codon, but the proteins that use UGA for selenocysteine usually have mRNA with significant secondary structure around the UGA. This may cause the ribosome to not recognize the UGA as a stop codon, allowing the selenocysteinyl-tRNA to incorporate the amino acid at that point. Normally UGA is stop codon, but the proteins that use UGA for selenocysteine usually have mRNA with significant secondary structure around the UGA. This may cause the ribosome to not recognize the UGA as a stop codon, allowing the selenocysteinyl-tRNA to incorporate the amino acid at that point. |
| 12. |
13 |
 Tryptophan Tryptophan | Trp | W | UGG | 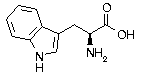 Tryptophan: Found in blood serum, gastric mucous membranes and especially in brain tissue, a precursor to Serotonin and used as an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Stimulates the smooth muscles, transmission of impulses between nerve cells, and in the regulation of cyclic body processes. Used in treatment of migraine headaches, insomnia and some types of depression. A balance must be maintained with other amino acids through dietary intake, or nutritional conflicts can occur. Tryptophan: Found in blood serum, gastric mucous membranes and especially in brain tissue, a precursor to Serotonin and used as an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Stimulates the smooth muscles, transmission of impulses between nerve cells, and in the regulation of cyclic body processes. Used in treatment of migraine headaches, insomnia and some types of depression. A balance must be maintained with other amino acids through dietary intake, or nutritional conflicts can occur. |
|
| Cytosine families |
Water |
|
| |
| 1. |
22 |
 Proline Proline | Pro | P | CCC CCU CCA CCG | 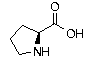 Proline: Major constituent of collagen, the main fibrous protein found in bone, cartilage and other connective tissue. Used in the maintenance and repair of joints and tendons. Proline: Major constituent of collagen, the main fibrous protein found in bone, cartilage and other connective tissue. Used in the maintenance and repair of joints and tendons. |
| 2. |
n |
 Leucine Leucine | Leu | L | CUC CUU CUA CUG |  4-Leucine: It is found in high concentrations in muscle tissue, and promotes wound healing of skin and bone. 4-Leucine: It is found in high concentrations in muscle tissue, and promotes wound healing of skin and bone. |
| 3. |
21 |
 Histidine Histidine | His | H | CAC CAU | 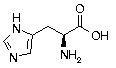 Histidine: Important in production of red and white blood cells, is abundant in hemoglobin, also the oxygen carrying pigment of red blood cells. Effective in treating allergic diseases. Helps remove heavy metals from tissues by chelation to trace minerals. Histidine: Important in production of red and white blood cells, is abundant in hemoglobin, also the oxygen carrying pigment of red blood cells. Effective in treating allergic diseases. Helps remove heavy metals from tissues by chelation to trace minerals. |
|
| 4. |
20 |
 Glutamine Glutamine | Gln | Q | CAA CAG | 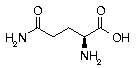 Glutamine: Readily passing through the blood brain barrier, it picks up ammonia in the central nervous system and delivers it to kidneys for deanimation. Used to protect against the poisonous effects of alcohol, and in the treatment of schizophrenia and senility. Also found in the intestinal tract. Glutamine: Readily passing through the blood brain barrier, it picks up ammonia in the central nervous system and delivers it to kidneys for deanimation. Used to protect against the poisonous effects of alcohol, and in the treatment of schizophrenia and senility. Also found in the intestinal tract. |
| 5. |
n |
 Arginine Arginine | Arg | R | CGC CGU CGA CGG | 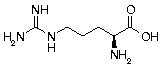 4-Arginine: Stimulates the immune system, promotes wound healing, and blocks formation of tumors. In the Anterior Pituitary gland, causes release of growth hormones. Increases spermatogenesis in sex glands. Also promotes detoxification of ammonia, and is involved in liver regeneration. 4-Arginine: Stimulates the immune system, promotes wound healing, and blocks formation of tumors. In the Anterior Pituitary gland, causes release of growth hormones. Increases spermatogenesis in sex glands. Also promotes detoxification of ammonia, and is involved in liver regeneration. |
| Adenine families |
Fire |
|
| |
| 13. |
12 |
 Threonine Threonine | Thr | T | ACC ACU ACA ACG | 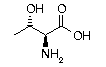 Threonine: Must be kept in balance with other amino acids through dietary intake, or nutritional conflicts may occur. In the liver, it acts as a lipotropic agent to help prevent fatty build ups. An important constituent of collagen, elastin and enamel proteins. Threonine: Must be kept in balance with other amino acids through dietary intake, or nutritional conflicts may occur. In the liver, it acts as a lipotropic agent to help prevent fatty build ups. An important constituent of collagen, elastin and enamel proteins. |
| 14. |
11 |
 Isoleucine Isoleucine | Ile | I | AUC AUU AUA | 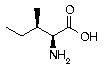 Isoleucine: It is found in high concentrations in muscle tissue. Since the only source is through dietary intake, it must be kept in balance proportion with other amino acids, or nutritional conflicts may occur. Isoleucine: It is found in high concentrations in muscle tissue. Since the only source is through dietary intake, it must be kept in balance proportion with other amino acids, or nutritional conflicts may occur. |
| 15. |
10 |
 Methionine* Methionine* | Met | M | AUG | 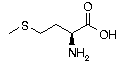 Methionine: Functions as a antioxidant (free radical deactivator) and neutralizes toxins. Helps guard against disorders of the skin and nails, prevents hair loss, and curbs accumulations of fat in the liver. Methionine: Functions as a antioxidant (free radical deactivator) and neutralizes toxins. Helps guard against disorders of the skin and nails, prevents hair loss, and curbs accumulations of fat in the liver. |
|
| 16. |
9 |
 Asparagine Asparagine | Asn | N | AAC AAU | 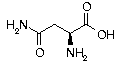 Asparagine: Participates in the metabolic control of cells functions in the brain and nervous system, thus used in treatment of brain and nervous system disorders. Asparagine: Participates in the metabolic control of cells functions in the brain and nervous system, thus used in treatment of brain and nervous system disorders. |
| 17. |
8 |
 Lysine Lysine | Lys | K | AAA AAG | 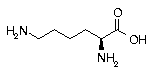 Lysine: Assures adequate absorption of the mineral calcium, and assists in promoting bone growth. Must be kept in balance with other amino acids through dietary intake, or nutritional conflicts may occur. Helps to form collagen, the fibrous protein constituent of bones, cartilage, tendons, and other connective tissues. Also used in treatment of Herpes Simplex. Lysine: Assures adequate absorption of the mineral calcium, and assists in promoting bone growth. Must be kept in balance with other amino acids through dietary intake, or nutritional conflicts may occur. Helps to form collagen, the fibrous protein constituent of bones, cartilage, tendons, and other connective tissues. Also used in treatment of Herpes Simplex. |
|
| n. |
7 |
 Serine Serine | Ser | S | AGC AGU |  2-Serine: Assist in the manufacture of the organic acid Creatine, found in blood, while also present within muscle and brain tissue as an energy source for muscle contraction. Participant in purine, pyrimidine and porphyrin biosynthesis. Also a natural moisturizing agent used in cosmetics. 2-Serine: Assist in the manufacture of the organic acid Creatine, found in blood, while also present within muscle and brain tissue as an energy source for muscle contraction. Participant in purine, pyrimidine and porphyrin biosynthesis. Also a natural moisturizing agent used in cosmetics. |
|
| n. |
6 |
 Arginine Arginine | Arg | R | AGA AGG | 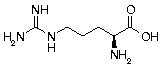 2-Arginine: Stimulates the immune system, promotes wound healing, and blocks formation of tumors. In the Anterior Pituitary gland, causes release of growth hormones. Increases spermatogenesis in sex glands. Also promotes detoxification of ammonia, and is involved in liver regeneration. 2-Arginine: Stimulates the immune system, promotes wound healing, and blocks formation of tumors. In the Anterior Pituitary gland, causes release of growth hormones. Increases spermatogenesis in sex glands. Also promotes detoxification of ammonia, and is involved in liver regeneration. |
|
| Guanine families |
Air |
|
| |
| 18. |
5 |
 Alanine Alanine | Ala | A | GCC GCU GCA GCG | 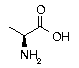 Alanine: Used in maintaining blood glucose levels by converting carbohydrates stored in liver and muscle tissue into glucose needed by the body to satisfy its energy needs. Also used as a food seasoning. Alanine: Used in maintaining blood glucose levels by converting carbohydrates stored in liver and muscle tissue into glucose needed by the body to satisfy its energy needs. Also used as a food seasoning. |
| 19. |
4 |
 Valine Valine | Val | V | GUC GUU GUA GUG | 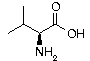 Valine: Used to treat severe amino acid deficiencies caused by addictions. One of the branched chain amino acids found in high concentration in muscle tissue. Valine: Used to treat severe amino acid deficiencies caused by addictions. One of the branched chain amino acids found in high concentration in muscle tissue. |
| 20. |
3 |
 Aspartic acid Aspartic acid | Asp | D | GAC GAU | 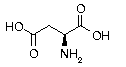 Aspartic Acid: Nitrogen derived from Aspartic Acid is used to form ribonucleotides, precursors to RNA and DNA. Aids in the disposal and detoxification of ammonia in the body. Also increases overall resistance to fatigue. Aspartic Acid: Nitrogen derived from Aspartic Acid is used to form ribonucleotides, precursors to RNA and DNA. Aids in the disposal and detoxification of ammonia in the body. Also increases overall resistance to fatigue. |
| 21. |
2 |
 Glutamic acid Glutamic acid | Glu | E | GAA GAG | 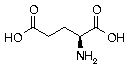 Glutamic Acid: Approximately 50% of the amino acid composition in the brain is represented by GLU and it’s derivatives. Used to transport potassium across the blood brain barrier. This amino acid acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, so is essentially fuel for the brain. Also found in stomach. Glutamic Acid: Approximately 50% of the amino acid composition in the brain is represented by GLU and it’s derivatives. Used to transport potassium across the blood brain barrier. This amino acid acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, so is essentially fuel for the brain. Also found in stomach. |
| 22. |
1 |
 Glycine Glycine | Gly | G | GGC GGU GGA GGG |  Glycine: Helps in the formation of the purine skeleton utilized in constructing RNA and DNA strands. Inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Stimulates the release of growth hormone, and aids in synthesis of hemoglobin. Used as food additive for a sweeter taste, is also effective for hyperacidity in the stomach (used in antacids). Glycine: Helps in the formation of the purine skeleton utilized in constructing RNA and DNA strands. Inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Stimulates the release of growth hormone, and aids in synthesis of hemoglobin. Used as food additive for a sweeter taste, is also effective for hyperacidity in the stomach (used in antacids). |
| |
|
|
|
| | |
| |
|
|
|
| | |
A code snippet of the one letter Amino acid abreviations
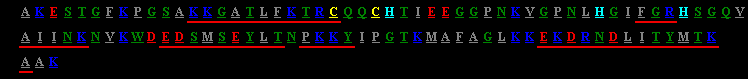
|
|
hydrophobic
hydrophilic
acidic
basic
histidin
cysteine
|